Introduction to Periodontal Diseases
Periodontal diseases, also known as gum diseases, affect the tissues that support your teeth. These conditions can harm your gums, bone, and the roots of your teeth. In fact, gum diseases are a leading cause of tooth loss in adults. Early care can help prevent serious problems. For this reason, understanding gum health is important for everyone.
What are Periodontal Diseases?
Periodontal diseases are infections of the gums and nearby structures. The most common types are gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is a mild form that causes red and swollen gums. However, if left untreated, it can turn into periodontitis. This advanced stage can damage the bone that holds your teeth. As a result, teeth may become loose or fall out.
Common Symptoms of Gum Diseases
Recognizing the signs early can help you get treatment sooner. Some symptoms may be mild at first. Still, it is important to pay attention to changes in your mouth. Watch for these signs:Red, swollen, or tender gumsBleeding while brushing or flossingBad breath that does not go awayReceding gums or longer-looking teethLoose or shifting teethPain when chewingSensitive teeth
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should see a dentist soon. Early action can prevent further damage.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
Gum diseases usually start with plaque. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If not removed, it can harden into tartar. Tartar makes it harder to clean your teeth and can lead to infection. Several factors can raise your risk:Poor oral hygiene habitsSmoking or using tobaccoDiabetes or other health conditionsFamily history of gum diseaseHormonal changes, such as pregnancyMedications that reduce saliva flowStress, which can weaken your immune system
Because these factors can add up, it is important to manage your overall health and habits.
How are Gum Diseases Diagnosed?
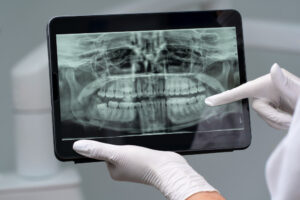
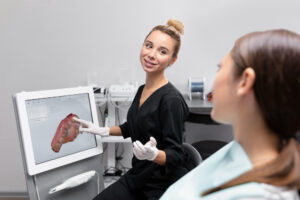
Dentists use several methods to check for gum problems. First, they will look at your gums for redness, swelling, or bleeding. Next, they may use a small tool to measure the space between your teeth and gums. Healthy gums have shallow spaces. Deeper spaces can mean gum disease. Sometimes, dentists take X-rays to see if bone has been lost. Regular dental check-ups help catch problems early.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Diseases
Treatment depends on how severe the disease is. For mild cases, better brushing and flossing may be enough. Dentists may also do a professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. In more serious cases, you may need:Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning below the gum line)Medications, such as mouth rinses or antibioticsSurgery to restore gum or bone tissue
After treatment, regular dental visits are important. This helps keep your gums healthy and prevents the disease from coming back.
Prevention Tips for Healthy Gums
Good habits can help you avoid gum diseases. Try these simple steps:Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpasteFloss daily to remove plaque between teethVisit your dentist for regular check-ups and cleaningsEat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and mineralsAvoid smoking or using tobacco productsManage health conditions like diabetes
Because prevention is easier than treatment, these steps can protect your smile for years to come.
Summary
In summary, periodontal diseases are common but preventable. Early signs include red or bleeding gums. Causes range from poor oral hygiene to health conditions. Dentists diagnose gum diseases with exams and X-rays. Treatments include cleaning, medication, or surgery. However, daily care and regular dental visits are the best ways to keep your gums healthy.
When to See a Dental Specialist
If you notice any signs of gum disease, do not wait. Consult a dental specialist for personalized advice on gum health. Early care can save your teeth and improve your overall well-being.