What is Bruxism?
Bruxism is the medical term for teeth grinding or jaw clenching. Many people do this while they sleep, but it can also happen during the day. Often, people do not realize they have bruxism until symptoms appear. Because bruxism can damage teeth and cause jaw pain, it is important to understand this condition. Early awareness helps prevent long-term problems.
Common Symptoms of Bruxism
Bruxism symptoms can be mild or severe. Sometimes, they are hard to notice at first. However, knowing what to look for can help you seek help sooner. Common signs include:Worn, flattened, or chipped teethJaw pain or tightness, especially in the morningHeadaches, often starting near the templesEar pain without infectionIncreased tooth sensitivitySleep problems or waking up tiredClicking or popping sounds in the jaw
Sometimes, people notice their partner grinding teeth at night. If you have any of these symptoms, it may be time to talk to a dentist.
Causes and Risk Factors
Bruxism can have many causes. Often, stress or anxiety plays a big role. But other factors may also lead to teeth grinding or jaw clenching. For example, some medicines or health conditions can increase your risk. Here are common causes and risk factors:High stress or anxiety levelsSleep problems, such as sleep apneaCaffeine or alcohol use, especially before bedSmoking or using recreational drugsCertain medicines, like antidepressantsFamily history of bruxismMisaligned teeth or bite problems
Because many factors can cause bruxism, it is important to look at your lifestyle and health history. Sometimes, more than one cause is involved.
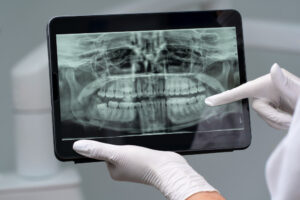
How Bruxism is Diagnosed
Diagnosing bruxism often starts with a dental checkup. Dentists look for signs of teeth grinding, such as worn enamel or jaw tenderness. They may also ask about your sleep habits and stress levels. In some cases, your dentist may:Ask about headaches or jaw painCheck for damage to the inside of your cheeksSuggest a sleep study if sleep problems are suspected
Early diagnosis helps prevent further damage. Therefore, regular dental visits are important for catching bruxism early.
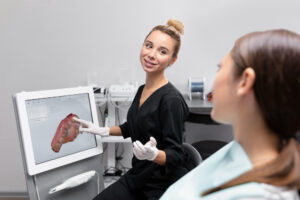
Effective Treatment Options
Bruxism treatment depends on the cause and severity. Many people find relief with simple changes or dental devices. Some common treatment options include:Wearing a mouth guard at night to protect teethManaging stress through relaxation techniquesCorrecting bite problems with dental workChanging medicines if they cause teeth grindingPhysical therapy for jaw musclesBotox injections for severe jaw clenching (in some cases)
Because each person is different, your dentist will suggest the best plan for you. According to the American Dental Association, mouth guards are often the first step.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
Simple lifestyle changes can help reduce bruxism symptoms. While not all cases can be prevented, these tips may help:Practice stress management, such as deep breathing or yogaAvoid caffeine and alcohol, especially in the eveningKeep a regular sleep scheduleDo not chew on pens or other objectsApply a warm washcloth to your jaw before bedTalk to your dentist about any new symptoms
Because prevention is easier than treatment, these habits can protect your teeth and jaw over time.
When to See a Dentist
If you notice signs of bruxism, do not wait to seek help. You should see a dentist if you:Have jaw pain or headaches that do not go awayNotice worn, chipped, or sensitive teethHear clicking or popping in your jawWake up feeling tired or with sore jaw muscles
Early treatment can prevent serious damage. Therefore, regular dental checkups are important for everyone.
In summary, bruxism can harm your teeth and jaw if left untreated. However, many treatment options and lifestyle changes can help. Consult a dentist for personalized advice on managing bruxism.